A) foraminiferan
B) radiolarian
C) ciliate
D) kinetoplastid
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A P. bursaria cell that has lost its zoochlorellae is aposymbiotic. If aposymbiotic cells have population growth rates the same as those of healthy, zoochlorella-containing P. bursaria in well-lit environments with plenty of prey items, then such an observation would be consistent with which type of relationship?
A) parasitic
B) competitive
C) toxic
D) mutualistic
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups is matched with a correct anatomical feature?
A) foraminifera → silicon-rich tests
B) dinoflagellata → holdfast
C) diatoms → tests made of cellulose
D) brown algae → blade
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Super cells characteristic of plasmodial slime molds result when which one of the following common cellular processes does not occur?
A) mitosis
B) cytokinesis
C) aerobic metabolism
D) endocytosis
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following data: (a) Most ancient eukaryotes are unicellular. (b) All eukaryotes alive today have a nucleus and cytoskeleton. (c) Most ancient eukaryotes lack a cell wall. Which of the following conclusions could reasonably follow the data presented? The first eukaryote may have been ________.
A) very similar to a plant cell
B) anaerobic
C) capable of phagocytosis
D) photosynthetic
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
SAR is a group defined by DNA similarities. This grouping represents ________.
A) a paraphyletic group
B) a hypothesis about evolutionary history
C) a catch-all group that links many unrelated organisms
D) a demonstration that DNA similarities cannot reveal evolutionary history
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dinoflagellates ________.
A) possess two flagella
B) are all autotrophic
C) lack mitochondria
D) include species that cause malaria
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs of protists and their ecological roles are correctly matched?
A) apicomplexans-parasites of animals
B) euglenozoans-primarily mixotrophic
C) dinoflagellates-parasites of plants
D) entamoebas-free-living soil organisms
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the phylogeny presented in this chapter, which protists are in the same eukaryotic supergroup as plants?
A) green algae
B) dinoflagellates
C) red algae
D) both A and C
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are given four test tubes, each containing an unknown protist, and your task is to read the following description and match these four protists to the correct test tube. When light, especially red and blue light, is shone on the tubes, oxygen bubbles accumulate on the inside of test tubes 1 and 2. Chemical analysis of test tube 1 indicates the presence of a chemical that is toxic to fish and humans. Chemical analysis of test tube 2 indicates the presence of substantial amounts of silica. Microscopic analysis of organisms in test tubes 1, 3, and 4 reveals the presence of permanent, membrane-bounded sacs just under the plasma membrane. Microscopic analysis of organisms in test tube 3 reveals the presence of an apicoplast in each. Microscopic analysis of the contents in test tube 4 reveals the presence of one large nucleus and one small nucleus in each organism. Test tube 4 contains ________.
A) Paramecium
B) Pfiesteria (dinoflagellate)
C) Entamoeba
D) Plasmodium
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following description and table to answer the question.
Diatoms are encased in petri-plate-like cases (valves) made of translucent hydrated silica whose thickness can be varied. The material used to store excess calories can also be varied. At certain times, diatoms store excess calories in the form of the liquid polysaccharide, laminarin, and at other times as oil. The following are data concerning the density (specific gravity) of various components of diatoms, and of their environment.
Specific Gravities of Materials Relevant to Diatoms
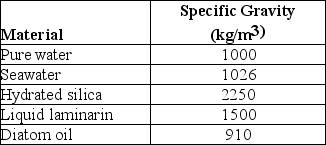 Water's density and, consequently, its buoyancy decrease at warmer temperatures. Considering the impact of temperature, and the table above, in which environment should diatoms sinking be slowest?
Water's density and, consequently, its buoyancy decrease at warmer temperatures. Considering the impact of temperature, and the table above, in which environment should diatoms sinking be slowest?
A) cold fresh water
B) warm fresh water
C) cold seawater
D) warm seawater
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trypanosome infections evade attacks by host immune systems through which of the following mechanisms?
A) production of new cell-surface proteins with a different molecular structure by each new generation
B) production of toxins that kill lymphocytes
C) insertion of its DNA into the nuclear DNA of host cells
D) infection of lymphocytes leading to a decline in the host's ability to fight infection
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Green algae differ from land plants in that many green algae ________.
A) are unicellular
B) have plastids
C) have alternation of generations
D) have cell walls containing cellulose
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chloroplasts of land plants are thought to have been derived according to which evolutionary sequence?
A) cyanobacteria → green algae → land plants
B) cyanobacteria → green algae → fungi → land plants
C) red algae → brown algae → green algae → land plants
D) cyanobacteria → red algae → green algae → land plants
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are given four test tubes, each containing an unknown protist, and your task is to read the following description and match these four protists to the correct test tube. When light, especially red and blue light, is shone on the tubes, oxygen bubbles accumulate on the inside of test tubes 1 and 2. Chemical analysis of test tube 1 indicates the presence of a chemical that is toxic to fish and humans. Chemical analysis of test tube 2 indicates the presence of substantial amounts of silica. Microscopic analysis of organisms in test tubes 1, 3, and 4 reveals the presence of permanent, membrane-bounded sacs just under the plasma membrane. Microscopic analysis of organisms in test tube 3 reveals the presence of an apicoplast in each. Microscopic analysis of the contents in test tube 4 reveals the presence of one large nucleus and one small nucleus in each organism. Test tube 1 contains ________.
A) Paramecium
B) Pfiesteria (dinoflagellate)
C) Entamoeba
D) Plasmodium
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella ________.
A) have the same evolutionary origin
B) have different structures
C) require different sources of energy
D) contain their own DNA
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following description and table to answer the question.
Diatoms are encased in petri-plate-like cases (valves) made of translucent hydrated silica whose thickness can be varied. The material used to store excess calories can also be varied. At certain times, diatoms store excess calories in the form of the liquid polysaccharide, laminarin, and at other times as oil. The following are data concerning the density (specific gravity) of various components of diatoms, and of their environment.
Specific Gravities of Materials Relevant to Diatoms
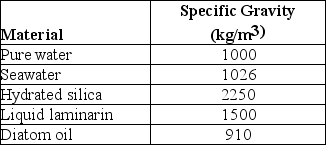 Water's density and, consequently, its buoyancy decrease at warmer temperatures. Based on this consideration, and using data from the table above, at which time of year should one expect diatoms to be storing excess calories mostly as oil?
Water's density and, consequently, its buoyancy decrease at warmer temperatures. Based on this consideration, and using data from the table above, at which time of year should one expect diatoms to be storing excess calories mostly as oil?
A) mid-winter
B) early spring
C) late summer
D) late fall
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the question.
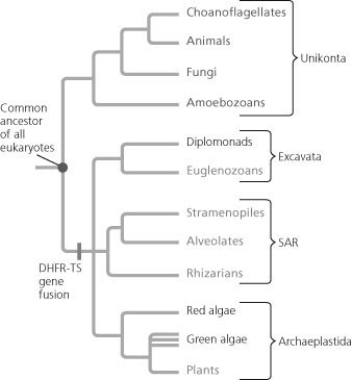 "Rare events" can help us understand evolutionary events, as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements explains the logic of this approach?
"Rare events" can help us understand evolutionary events, as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements explains the logic of this approach?
A) Organisms with the mutation evolved convergently.
B) The mutation provided an adaptive advantage to the organisms that contained it.
C) Because the mutation likely occurred only once, all organisms with the mutation have a common ancestor with the mutation.
D) "Reverse evolution" does not occur.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which group is incorrectly paired with its description?
A) diatoms-important producers in aquatic communities
B) red algae-eukaryotes that acquired plastids by secondary endosymbiosis
C) apicomplexans-unicellular parasites with intricate life cycles
D) diplomonads-unicellular eukaryotes with modified mitochondria
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to determine the "root" of the eukaryote phylogenetic tree, scientists should ________.
A) compare the myosin genes in amoebozoans and opisthokonts
B) compare the sequences of chloroplast genes of green algae and plants
C) sequence more nuclear genes in green algae and plants
D) sequence more nuclear genes in slime molds and other unikonts
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams