A) $500 and that the other player gets $500.
B) $998 and that the other player gets $2.
C) $999 and that the other player gets $1.
D) $1000 and that the other player gets nothing.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his 1951 book Social Choice and Individual Values,Arrow's perfect voting system satisfies all of the following properties except
A) unanimity.
B) transitivity.
C) reflexivity.
D) independence of irrelevant alternatives.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If preferences exhibit the property of transitivity,then
A) the preferences are irrational.
B) individuals prefer more government involvement in private markets than do people whose preferences are not transitive.
C) preferences change over time more quickly than when preferences are not transitive.
D) preferences satisfy one of the properties assumed to be desirable by Kenneth Arrow in Social Choice and Individual Values.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet paradox shows that
A) allocations of resources based on majority rule are always inefficient.
B) problems in counting votes can negate legitimate democratic outcomes.
C) the order on which things are voted can affect the result.
D) transitive preferences are inconsistent with rationality.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-14
The Johnson family is planning a vacation and, though Mr. and Mrs. Johnson will be paying for the trip, they have decided to use a democratic voting process to choose their destination. The family members' preferences are reflected in the table below.
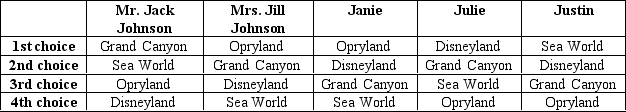 -Refer to Table 22-14.Mr.Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule and proposes first choosing between Opryland and the Grand Canyon,then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Sea World,and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Disneyland.If everyone votes according to their preferences,
-Refer to Table 22-14.Mr.Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule and proposes first choosing between Opryland and the Grand Canyon,then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Sea World,and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Disneyland.If everyone votes according to their preferences,
A) the winner of the first vote will be Opryland, the winner of the second vote will be Sea World, and the winner of the final vote will be Disneyland.
B) the winner of the first vote will be Grand Canyon, the winner of the second vote will be Grand Canyon, and the winner of the final vote will be Disneyland.
C) the winner of the first vote will be Grand Canyon, the winner of the second vote will be Sea World, and the winner of the final vote will be Disneyland.
D) the winner of the first vote will be Grand Canyon, the winner of the second vote will be Grand Canyon, and the winner of the final vote will be Grand Canyon.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economist Kenneth Arrow wrote a famous book in 1951 in which he took up the question,
A) Is there a perfect voting system?
B) Are preferences transitive?
C) Is a dictatorship a good form of government?
D) Should the president of the United States be elected to a single, six-year term?
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a moral hazard problem?
A) A manager stays late one evening so that her employee can leave early to attend his child's music recital.
B) A small child takes an extra cookie from the cookie jar when he thinks his mom isn't watching him closely.
C) An employee plays solitaire on her computer at 4:30 p.m. on a Friday when her boss has left for the day.
D) A customer whose new eyeglasses come with a "60-day insurance policy in case of breakage" leaves her glasses out where her new puppy can chew on them.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The moral hazard problem and the desire of firms to lessen that problem serve as a plausible explanation for a firm paying above-equilibrium wages to its workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In corporations,which of the following are agents but not principals?
A) shareholders
B) the board of directors
C) managers
D) workers
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-13
The fortunate residents of Anytown have a budget surplus. The mayor decided that it is only fair to have the residents vote on what to do with the surplus. The mayor has narrowed the options down to three possible projects: a playground, a library, or a swimming pool. The voters fall into three categories and have preferences as illustrated in the table.
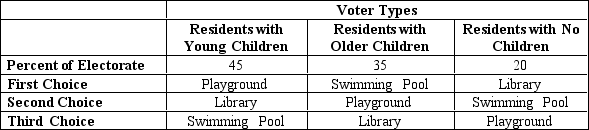 -Refer to Table 22-13.If the mayor asks the residents to choose between the playground and the library using pairwise voting,
-Refer to Table 22-13.If the mayor asks the residents to choose between the playground and the library using pairwise voting,
A) the playground wins by 45%.
B) the playground wins by 60%.
C) the library wins by 20%.
D) the library wins by 80%.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The problem that arises when one person performs a task on behalf of another person is called
A) the hidden characteristics problem.
B) the lemons problem.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The field of political economy
A) applies the methods of political science to microeconomics.
B) applies the methods of political science to macroeconomics.
C) is relevant to the issue of how active government should be in economic matters.
D) integrates psychological insights to better understand individual choices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Insurance companies charge annual premiums to collect revenue,which they then use to pay customers who file claims for damages they incur.As a result of the moral hazard problem (1) what is the effect on the percentage of policy holders making claims,and (2) what is the effect on the average premium charged when compared to a world with no moral hazard problem?
A) The percentage of policy holders making claims is higher; average annual premiums are lower.
B) The percentage of policy holders making claims is lower; average annual premiums are lower.
C) The percentage of policy holders making claims is higher; average annual premiums are higher.
D) The percentage of policy holders making claims is lower; average annual premiums are higher.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economic models incorporate the assumption of rational behavior on the part of economic actors.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics,a difference in access to relevant knowledge is called a(n)
A) relevancy frontier.
B) knowledge gap.
C) information asymmetry.
D) information equilibrium.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-4
Five voters must choose from among four options: A, B, C, or D. Each voter's preferences are summarized in the table below. Options higher in the table are more preferred by the voter.
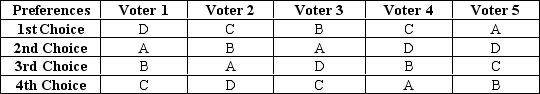 -Refer to Table 22-4.Which pairwise voting scheme would result in outcome A?
-Refer to Table 22-4.Which pairwise voting scheme would result in outcome A?
A) First, choose between A and B. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and D.
B) First, choose between A and C. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and B. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and D.
C) First, choose between B and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and A.
D) First, choose between C and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and A. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and B.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An implication of the median voter theorem is that
A) minority views and majority views are given equal weight.
B) platforms of the major political parties will not differ greatly.
C) the logic of democracy is fundamentally flawed.
D) behavioral economics plays a significant role in voting outcomes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-4
Five voters must choose from among four options: A, B, C, or D. Each voter's preferences are summarized in the table below. Options higher in the table are more preferred by the voter.
 -Refer to Table 22-4.Which pairwise voting scheme would result in outcome D?
-Refer to Table 22-4.Which pairwise voting scheme would result in outcome D?
A) First, choose between A and B. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and D.
B) First, choose between B and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and A.
C) First, choose between C and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and A. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and B.
D) First, choose between C and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and B. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and A.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rick goes to work 8 hours per day,but while he is at work he spends most of his time visiting internet sites monitoring his fantasy football teams.This is an example of
A) the Condorcet Paradox.
B) signaling.
C) moral hazard.
D) screening.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A woman gives her boyfriend a birthday present.The gift could be viewed by the boyfriend as a
A) moral hazard problem.
B) screening device.
C) signal of how much she cares for him.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 353
Related Exams