A) decrease interest rates.
B) result in a net decrease in aggregate demand.
C) crowd out investment spending by business firms.
D) decrease money demand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,if the price level decreases,then
A) the interest rate falls because money demand shifts right.
B) the interest rate falls because money demand shifts left.
C) the interest rate rises because money supply shifts right.
D) the interest rate rises because money supply shifts left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the money-supply curve would shift rightward
A) if the money demand curve shifted right.
B) if the Federal Reserve chose to increase the money supply.
C) if the interest rate increased.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the money-supply curve is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-5.On the figure,MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand. 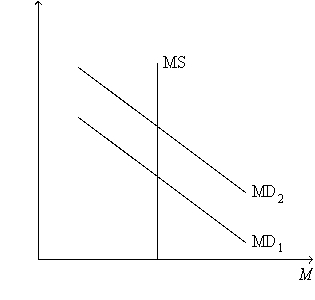 -Refer to Figure 24-5.What is measured along the vertical axis of the graph?
-Refer to Figure 24-5.What is measured along the vertical axis of the graph?
A) the quantity of output
B) the amount of crowding out
C) the interest rate
D) the price level
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,a decrease in the price level shifts the
A) money demand curve rightward,so the interest rate increases.
B) money demand curve rightward,so the interest rate decreases.
C) money demand curve leftward,so the interest rate decreases.
D) money demand curve leftward,so the interest rate increases.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest-rate effect
A) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services supplied.
C) is responsible for the downward slope of the money-demand curve.
D) is the least important reason,in the case of the United States,for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is an increase in government expenditures,which of the following raises investment spending?
A) the investment accelerator and crowding out
B) the investment accelerator but not crowding out
C) crowding out but not the investment accelerator
D) neither the investment accelerator or crowding out
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If it were not for the automatic stabilizers in the U.S.economy,
A) the Federal Reserve would have less reason than it has now to monitor stock prices.
B) it would be more desirable than it is now for the Federal Reserve to target an interest rate.
C) a strict balanced-budget rule would be more desirable than it is now.
D) output and employment would probably be more volatile than they are now.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume there is a multiplier effect,some crowding out,and no accelerator effect.An increase in government expenditures changes aggregate demand more,
A) the smaller the MPC and the stronger the influence of income on money demand.
B) the smaller the MPC and the weaker the influence of income on money demand.
C) the larger the MPC and the stronger the influence of income on money demand.
D) the larger the MPC and the weaker the influence of income on money demand.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government buys new weapons systems.The manufacturers of weapons pay their employees.The employees spend this money on goods and services.The firms from which the employees buy the goods and services pay their employees.This sequence of events illustrates
A) the accelerator effect.
B) the multiplier effect.
C) the chain effect.
D) the bandwagon effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the U.S.economy,which of the following is the most important reason for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve?
A) the wealth effect
B) the interest-rate effect
C) the exchange-rate effect
D) the real-wage effect
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions,use the diagram below:
Figure 24-7. 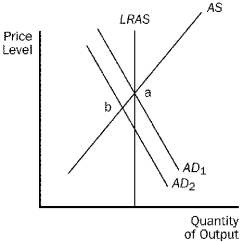 -Refer to Figure 24-7.If the economy is at point b,a policy to restore full employment would be
-Refer to Figure 24-7.If the economy is at point b,a policy to restore full employment would be
A) an increase in the money supply.
B) a decrease in government purchases.
C) an increase in taxes.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed decreases the money supply,we expect
A) interest rates and stock prices to rise.
B) interest rates and stock prices to fall.
C) interest rates to rise and stock prices to fall.
D) interest rates to fall and stock prices to rise.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People choose to hold a smaller quantity of money if
A) the interest rate rises,which causes the opportunity cost of holding money to rise.
B) the interest rate falls,which causes the opportunity cost of holding money to rise.
C) the interest rate rises,which causes the opportunity cost of holding money to fall.
D) the interest rate falls,which causes the opportunity cost of holding money to fall.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the money supply shifts the aggregate-supply curve to the right.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When government expenditures increase,the interest rate
A) increases,making the change in aggregate demand larger.
B) increases,making the change in aggregate demand smaller
C) decreases,making the change in aggregate demand larger.
D) decreases,making the change in aggregate demand smaller.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is likely that a constitutional amendment that required the government always to run a balanced budget would
A) contribute to a more stable level of output.
B) mitigate the crowding-out effect.
C) eliminate the economy's automatic stabilizers.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is defined as the fraction of
A) extra income that a household consumes rather than saves.
B) extra income that a household either consumes or saves.
C) total income that a household consumes rather than saves.
D) total income that a household either consumes or saves.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to their impact on aggregate demand for the U.S.economy,which of the following represents the correct ordering of the wealth effect,interest-rate effect,and exchange-rate effect from most important to least important?
A) wealth effect,exchange-rate effect,interest-rate effect
B) exchange-rate effect,interest-rate effect,wealth effect
C) interest-rate effect,wealth effect,exchange-rate effect
D) interest-rate effect,exchange-rate effect,wealth effect
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 415
Related Exams