A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
C) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole
D) dispersion forces, ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole
E) None. Since both are gases at room temperature, they do not interact with each other.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling point.
A) Br2
B) N2
C) Cl2
D) O2
E) H2
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Boron triiodide (BI3) melts at 49.9 °C and boils at 209.5 °C at a constant pressure of 1 atm. What state of matter must a sample of boron triiodide be in at 100°C and 1 atm?
A) liquid
B) gas
C) solid
D) solid and liquid in equilibrium
E) liquid and gas in equilibrium
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ________ liquid crystal has the least order and is the most liquid-like.
A) nematic
B) smectic
C) cholesteric
D) smectic B
E) smectic C
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
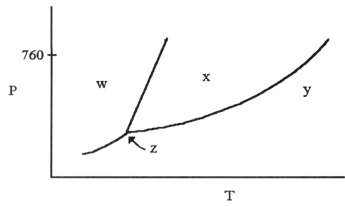 -The phase diagram of a substance is given above. The region that corresponds to the solid phase is ________.
-The phase diagram of a substance is given above. The region that corresponds to the solid phase is ________.
A) w
B) x
C) y
D) z
E) x and y
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they have ________ attraction for one another.
A) more separated, more
B) more separated, less
C) closer together, more
D) closer together, less
E) larger, greater
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics would prevent liquid crystal behavior?
A) long axial structure
B) ionic configuration
C) carbon-carbon single bonds
D) double bonding
E) polar groups
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
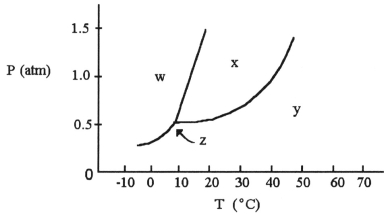 -The normal boiling point of the substance with the phase diagram shown above is ________ °C.
-The normal boiling point of the substance with the phase diagram shown above is ________ °C.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 50
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following molecules is hydrogen bonding likely to be the most significant component of the total intermolecular forces?
A) CH4
B) C5H11OH
C) C6H13NH2
D) CH3OH
E) CO2
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following, ________ is the least volatile.
A) CI4
B) CF4
C) CBr4
D) CCl4
E) CH4
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
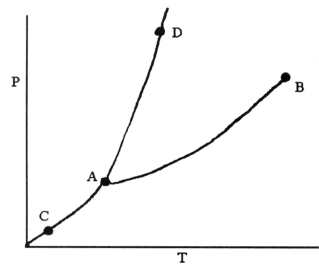 -On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point ________ correspond to the critical temperature and pressure.
-On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point ________ correspond to the critical temperature and pressure.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules has hydrogen bonding as its only intermolecular force?
A) HF
B) H2O
C) C6H13NH2
D) C5H11OH
E) None, all of the above exhibit dispersion forces.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The intermolecular force(s) responsible for the fact that CH4 has the lowest boiling point in the set CH4, SiH4, GeH4, SnH4 is/are ________.
A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole-dipole interactions
C) London dispersion forces
D) mainly hydrogen bonding but also dipole-dipole interactions
E) mainly London-dispersion forces but also dipole-dipole interactions
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What types of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and HF?
A) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
B) dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
C) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
D) dispersion forces
E) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a given substance that exhibits liquid-crystalline properties, the transition from solid to liquid-crystal state occurs ________.
A) over a range of temperatures between the melting point of the solid and the boiling point of the liquid
B) at the melting point of the solid
C) over a range of temperatures that includes the melting point of the solid
D) at a well-defined temperature above the melting point of the solid
E) at a well-defined temperature below the melting point of the solid
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the predominant intermolecular force in H2NNH2?
A) hydrogen bonding
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) ionic bonding
D) dipole-dipole attraction
E) London-dispersion forces
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
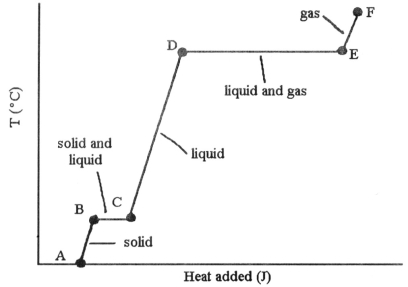 -The phase changes B → C and D ��→ E are not associated with temperature increases because the heat energy is used up to ________.
-The phase changes B → C and D ��→ E are not associated with temperature increases because the heat energy is used up to ________.
A) increase distances between molecules
B) break intramolecular bonds
C) rearrange atoms within molecules
D) increase the velocity of molecules
E) increase the density of the sample
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are ________.
A) very weak compared with kinetic energies of the molecules
B) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close together
C) strong enough to keep the molecules confined to vibrating about their fixed lattice points
D) not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other
E) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close together but not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact that ice is less dense than liquid water?
A) London dispersion forces
B) dipole-dipole forces
C) ion-dipole forces
D) hydrogen bonding
E) ionic bonding
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary action depends on ________.
A) the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and gravity
B) gravity alone
C) only the magnitude of adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube
D) the viscosity of the liquid
E) only the magnitude of cohesive forces in the liquid
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 124
Related Exams