A) there will be an increase in the equilibrium quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) there will be a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate.
C) the aggregate-demand curve will shift to the right.
D) fewer firms will choose to borrow to build new factories and buy new equipment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are effects of an increase in government spending financed by a tax increase?
A) the tax increase reduces consumption; the change in the interest rate reduces residential construction
B) the tax increase reduces consumption; the change in the interest rate raises residential construction
C) the tax increase raises consumption; the change in the interest rate reduces residential construction
D) the tax increase raises consumption; the change in the interest rate reduces residential construction.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sometimes during wars, government expenditures are larger than normal. To reduce the effects this spending creates on interest rates,
A) the Federal Reserve could increase the money supply by buying bonds.
B) the Federal Reserve could increase the money supply by selling bonds.
C) the Federal Reserve could decrease the money supply by buying bonds.
D) the Federal Reserve could decrease the money supply by selling bonds.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate would fall and the quantity of money demanded would
A) increase if there were a surplus in the money market.
B) increase if there were a shortage in the money market.
C) decrease if there were a surplus in the money market.
D) decrease if there were a shortage in the money market.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, if the price level decreases, then
A) the interest rate falls because money demand shifts right.
B) the interest rate falls because money demand shifts left.
C) the interest rate rises because money supply shifts right.
D) the interest rate rises because money supply shifts left.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, changes in the money supply affect
A) prices.
B) output.
C) unemployment rates.
D) All of the above.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Initially, the economy is in long-run equilibrium. Aggregate demand then shifts leftward by $50 billion. The government wants to increase its spending in order to avoid a recession. If the crowding-out effect is always half as strong as the multiplier effect, and if the MPC equals 0.8, then by how much do government purchases have to increase in order to offset the $50 billion leftward shift?
A) by $5 billion
B) by $10 billion
C) by $20 billion
D) by $50 billion
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In recent years, the Federal Reserve has conducted policy by setting a target for the
A) size of the money supply.
B) growth rate of the money supply.
C) federal funds rate.
D) discount rate.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Government expenditures on capital goods such as roads could increase aggregate supply. Such effects on aggregate supply are likely to matter more in the short run than in the long run.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC is 2/3 then the multiplier is
A) 3/2, so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $150.
B) 3/2, so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $150.
C) 3, so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $300.
D) 3, so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $300.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there were a large decline in net exports. If the Fed wanted to stabilize output, it could
A) buy bonds to raise interest rates.
B) buy bonds to lower interest rates.
C) sell bonds to raise interest rates.
D) sell bonds to lower interest rates.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A) an increase in the price level
B) an increase in the money supply
C) a decrease in the price level
D) a decrease in the money supply
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Opponents of active stabilization policy
A) generally don't believe, even in theory, that fiscal policy can stabilize the economy.
B) generally agree that fiscal policy has no impact in the long run.
C) believe some effects of monetary policy may be long-lived.
D) think the Fed should simply try to fine tune the economy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In response to the sharp decline in stock prices in October 1987, the Federal Reserve
A) increased interest rates, and the economy avoided a recession.
B) increased interest rates, but the economy was unable to avoid a recession.
C) decreased interest rates, and the economy avoided a recession.
D) decreased interest rates, but the economy was unable to avoid a recession.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If households view a tax cut as temporary, then the tax cut
A) has no affect on aggregate demand.
B) has more of an affect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
C) has the same affect as when households view the cut as permanent.
D) has less of an affect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following sequence of events: price level demand for money equilibrium interest rate quantity of goods and services demanded This sequence explains why the
A) money-supply curve is vertical.
B) aggregate-demand curve shifts leftward in response to a monetary injection.
C) aggregate-demand curve shifts rightward in response to a monetary injection.
D) aggregate-demand curve slopes downward.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-3.
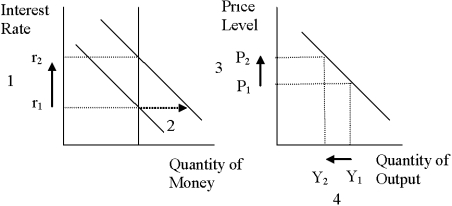 -Refer to Figure 16-3. For an economy such as the United States, what component of the demand for goods and services is most responsible for the decrease in output from Y1 to Y2?
-Refer to Figure 16-3. For an economy such as the United States, what component of the demand for goods and services is most responsible for the decrease in output from Y1 to Y2?
A) consumption
B) investment
C) net exports
D) government spending
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A) The price level rises.
B) The price level falls.
C) The money supply falls.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tends to make aggregate demand shift further to the right than the amount by which government expenditures increase?
A) the crowding-out effect
B) the multiplier effect
C) the exchange-rate effect
D) the interest-rate effect
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier is 6 and if there is no crowding-out effect, then a $60 billion increase in government expenditures causes aggregate demand to
A) increase by $250 billion.
B) increase by $333 billion.
C) increase by $360 billion.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 321 - 340 of 416
Related Exams