A) omitted variables.
B) reverse causality.
C) government propaganda.
D) medical incompetence.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Figure 2-23 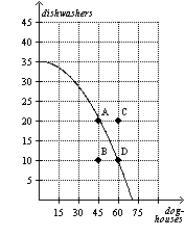 -Refer to Figure 2-23. Points B and C represent infeasible outcomes for this economy.
-Refer to Figure 2-23. Points B and C represent infeasible outcomes for this economy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Who would be more likely to study the inflation rate in the United States, a macroeconomist or a microeconomist?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-4 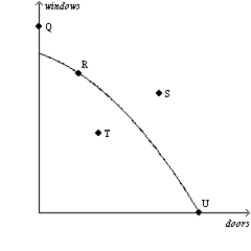 -Refer to Figure 2-4. This economy has the ability to produce at which points) ?
-Refer to Figure 2-4. This economy has the ability to produce at which points) ?
A) Q, R, T, U
B) R, T, U
C) R, U
D) T
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Factors of production are
A) the mathematical calculations firms make in determining their optimal production levels.
B) social and political conditions that affect production.
C) the physical relationships between economic inputs and outputs.
D) inputs into the production process.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about economic models is correct?
A) Economic models are built to mirror reality exactly.
B) Economic models are useful, but they should not be used for the purpose of improving public policies.
C) Because economic models omit many details, they allow us to see what is truly important.
D) Economic models seldom incorporate equations or diagrams.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists are trying to help improve the world, they are
A) in the realm of positive economics rather than normative economics.
B) in the realm of macroeconomics rather than microeconomics.
C) scientists.
D) policy advisers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
With the resources it has, an economy can produce at any point on or outside the production possibilities frontier, but it cannot produce at points inside the frontier.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-8 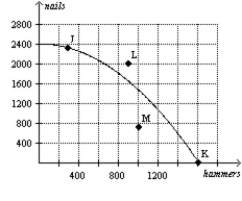 -Refer to Figure 2-8. Inefficient production is represented by which points) ?
-Refer to Figure 2-8. Inefficient production is represented by which points) ?
A) K, M
B) L
C) L, M
D) M
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic models
A) cannot be useful if they are based on false assumptions.
B) were once thought to be useful, but that is no longer true.
C) must incorporate all aspects of the economy if they are to be useful.
D) can be useful, even if they are not particularly realistic.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Historical episodes are not valuable to economists.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of a line passing through the points 15, 3) and 10, 6) is
A) -3/5.
B) 3/5.
C) -5/3.
D) 5/3.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the circular-flow diagram, firms produce
A) goods and services using factors of production.
B) output using inputs.
C) factors of production using goods and services.
D) Both a) and b) are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eva wants to create a graph containing the prices of concert tickets and the corresponding quantities of concert tickets demanded by customers. She should use an)
A) pie chart.
B) bar graph.
C) time-series graph
D) coordinate system.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-7 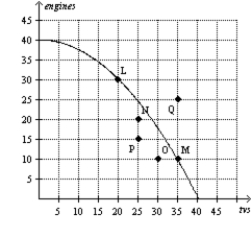 -Refer to Figure 2-7. If this economy moved from point P to point N, then
-Refer to Figure 2-7. If this economy moved from point P to point N, then
A) it still would not be producing efficiently.
B) there would be no gain in either engines or tvs.
C) it would be producing more engines and more tvs than at point P.
D) It is not possible for this economy to move from point P to point N without additional resources.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way to characterize the difference between positive statements and normative statements is as follows:
A) Positive statements tend to reflect optimism about the economy and its future, whereas normative statements tend to reflect pessimism about the economy and its future.
B) Positive statements offer descriptions of the way things are, whereas normative statements offer opinions on how things ought to be.
C) Positive statements involve advice on policy matters, whereas normative statements are supported by scientific theory and observation.
D) Economists outside of government tend to make normative statements, whereas government-employed economists tend to make positive statements.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When constructing a production possibilities frontier, which of the following assumptions is not made?
A) The economy produces only two goods or two types of goods.
B) Firms produce goods using factors of production.
C) The technology available to firms is given.
D) The quantities of the factors of production that are available are increasing over the relevant time period.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the circular-flow diagram, which of the following items represents a payment for a factor of production?
A) interest
B) capital
C) spending by households on goods
D) spending by households on services
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Figure 2-23  -Refer to Figure 2-23. Unemployment could cause this economy to produce at point B.
-Refer to Figure 2-23. Unemployment could cause this economy to produce at point B.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A macroeconomist - as opposed to a microeconomist - would study
A) the effects of rent control on housing in New York City.
B) the effects of foreign competition on the US auto industry.
C) the effects of borrowing by the federal government.
D) the effects of raising the gasoline tax on transit ridership.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 341 - 360 of 620
Related Exams